Think of it this way: old-school SEO was like a librarian who could only find a book if you knew the exact title. If you were off by a single word, you were out of luck. Semantic SEO is the modern librarian who listens to what you're trying to find, understands the context of your question, and not only finds the perfect book but also suggests a few related articles and a documentary you didn't even know you needed.
It's all about meaning, not just matching words.
Going Beyond Keywords With Semantic SEO

So, what is semantic SEO? It’s a shift in strategy. Instead of obsessing over a single keyword, we're building content around entire topics. We focus on the context surrounding those topics and, most importantly, the searcher's true intent. This approach helps search engines like Google understand the actual meaning of your content, which means you can rank for a much wider variety of searches.
This move from keywords to concepts is a massive part of modern digital marketing. It's the core idea behind getting your site found through things like AI Search Engine Optimization.
Why Context Matters More Than Keywords
In the early days of SEO, the game was much simpler. You could often win by just stuffing a keyword into a page over and over again. Those days are long gone. Search engines are incredibly sophisticated now, and they prioritize content that thoroughly answers a searcher's entire problem, not just the specific words they typed into the search bar.
The data backs this up. Websites that lean into semantic SEO have seen their featured snippet placements double. And consider this: Google now rewrites over 60% of title tags on its own to better align with what it believes the user is actually looking for. That’s a clear signal that they care more about intent than your perfectly crafted, keyword-matched title.
This evolution is central to what https://copymasters.co/blog/what-is-search-engine-optimization is today.
To get a feel for how different these two approaches are, let's break it down.
Traditional SEO vs Semantic SEO At a Glance
| Aspect | Traditional SEO | Semantic SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Specific, isolated keywords | Broad topics and user intent |
| Content Goal | Rank for a target keyword | Become a topical authority |
| Strategy | Keyword density and placement | Building a web of related concepts |
| Search Engine View | Sees a string of words | Understands the meaning and context |
| Outcome | Ranks for a few specific terms | Ranks for hundreds of related queries |
This table really highlights the shift. We're moving away from a narrow, rigid approach to one that's much more holistic and, frankly, more helpful to the user.
Adopting a semantic mindset gives you a serious edge:
- Deeper Relevance: Your content actually solves the user's problem, which creates a much better experience and keeps them on your site longer.
- Wider Reach: A single, well-crafted page can rank for hundreds of related long-tail keywords and questions you didn't even directly target.
- Future-Proofing: As search becomes more conversational and AI-driven, content that's rich in context will always have an advantage.
Ultimately, semantic SEO is about creating a network of meaningful, interconnected content. It’s how you prove to both users and search engines that you're a genuine authority in your field.
The Shift From Keywords To Concepts

To really get what semantic SEO is all about, you have to rewind the clock. Back in the day, SEO was a much simpler, almost mechanical game. The winning formula was to pick a keyword and cram it onto a page as many times as you could. We called it keyword stuffing.
This old-school strategy treated search engines like basic word-counters. If you wanted to rank for "best running shoes," you’d just repeat that exact phrase over and over in your title, headings, and text. Success was all about keyword density, and the actual quality of the content often took a backseat. Unsurprisingly, this led to a lot of spammy, unhelpful pages built for robots, not actual humans.
The Hummingbird Update: A Turning Point
Then, in 2013, everything changed. Google rolled out its Hummingbird update, which wasn't just a small adjustment—it was a complete rewrite of its core search algorithm. This was the moment semantic SEO was truly born. For the first time, Google could understand the meaning and context behind our searches, not just the words we used.
Instead of just looking at individual words, Hummingbird allowed Google to understand the meaning behind conversational queries. The search engine started thinking in concepts, not just keywords.
This one update made tactics like keyword stuffing instantly obsolete. A page no longer had to contain the exact phrase a user typed to rank. Google was now smart enough to figure out the intent behind a search and deliver the best answer, even if the wording was totally different.
Think about it: a search for "best place to see the Eiffel Tower" could now bring up articles about rooftop bars, scenic parks, or specific viewpoints, even if they never used that exact search phrase.
From Keywords To Entities
This evolution forced SEOs and content creators to completely rethink their approach. The game was no longer about optimizing for a single, isolated term. It was about building comprehensive resources around entire topics. Our approach to keyword research best practices had to grow up, fast.
The modern way of thinking, which is the heart of semantic SEO, is all about connecting entities. An entity is just a well-defined thing or concept: a person, a place, an idea, a product. By creating content that deeply covers a subject and all its related entities, you signal to Google that you're an authority. That’s how you win in search today.
Understanding The 3 Pillars Of Semantic SEO
To really get a handle on semantic SEO, you need to understand the three core ideas that make it work. Think of them as the legs of a stool—they all work together to build context, prove your expertise to search engines, and, most importantly, give your audience what they actually want. Getting these right is how you move from just chasing keywords to building real topical authority.
This visual does a great job of showing how the focus shifts from a narrow keyword-based approach to something much more holistic.
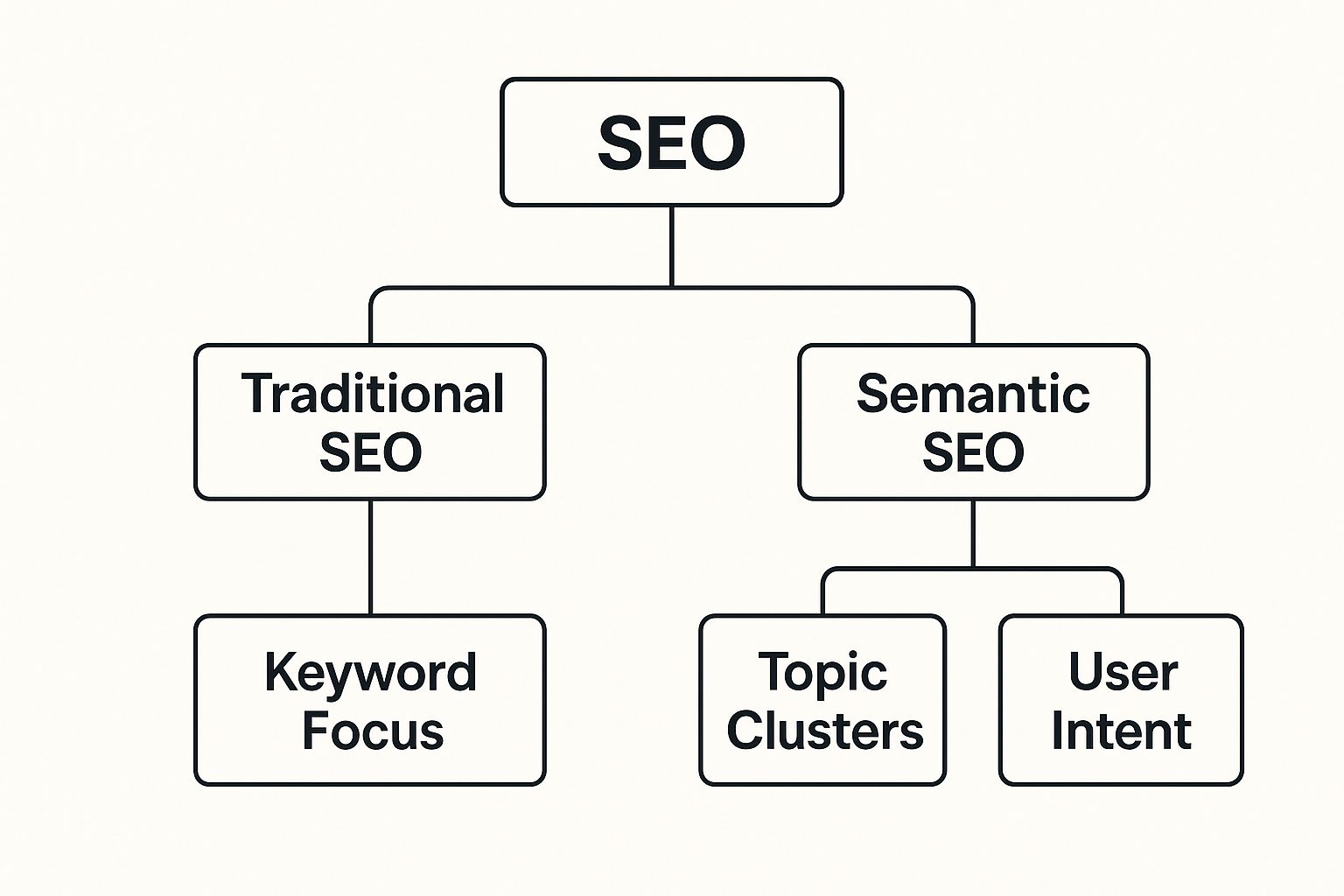
As you can see, old-school SEO was all about the keyword. The semantic approach is so much bigger, branching out to consider user intent and topic clusters to create a strategy that actually works today.
Pillar 1: User Intent
The first and most important pillar is user intent. This is the "why" behind every search. Instead of just seeing the words someone typed into the search bar, we have to figure out what they’re trying to do. This is the absolute foundation of semantic search.
Almost every search query boils down to one of four types of intent:
- Informational: The person is looking for an answer. Think "what is the capital of Australia?" or "how to bake sourdough bread."
- Navigational: They're trying to get to a specific website. A search for "Copy Masters login" or "YouTube" is a perfect example.
- Transactional: They have their wallet out and are ready to buy. Queries like "buy Nike Air Force 1" or "best SEO content service subscription" are clear signals.
- Commercial: They're in the research phase, comparing options before they make a purchase. You'll see searches like "best running shoes for flat feet" or "Copy Masters vs Surfer SEO."
The secret is to look at the search engine results page (SERP) for your target keywords. The results Google is already showing will tell you exactly what kind of intent it thinks users have, so you can create content that fits perfectly.
Pillar 2: Topic Clusters
Next up, we have the topic cluster model. This is simply a smarter way to organize your content to show search engines you're an expert on a subject. Instead of publishing a bunch of disconnected blog posts, you build a central "pillar page" that covers a broad topic from a high level.
Then, you support that pillar with a series of "cluster" articles, each one diving deep into a specific subtopic. The crucial part? Every cluster article links back to the main pillar page, creating a web of interconnected, authoritative content.
This structure sends a powerful signal to Google that your website isn't just a one-off source, but a comprehensive hub of information on a subject. It's how you prove expertise and help all the pages in that cluster rank higher.
This isn't just a nice-to-have; it's a core part of any modern semantic SEO strategy.
Pillar 3: Entities And The Knowledge Graph
Finally, the third pillar is all about entities and Google's Knowledge Graph. An entity is just a thing or concept that Google can uniquely identify—a person, place, brand, or idea. Think "Apple Inc.," "Mount Everest," or "photosynthesis."
The Knowledge Graph is Google's massive brain, a database connecting all these entities and understanding the relationships between them. It’s how Google knows that Steve Jobs is connected to Apple Inc., and that both are related to concepts like "technology" and "California."
When you include relevant entities and related concepts in your writing, you're giving Google the breadcrumbs it needs to connect the dots. This adds a rich layer of context, helping the search engine understand your page's meaning with far more confidence. The result? Better, more relevant rankings.
Putting Semantic SEO Into Action

Understanding the theory is great, but putting it into practice is where you’ll see the results. Shifting to a semantic SEO mindset means changing how you research, write, and structure your content to build a web of meaning across your entire site.
The goal? To create a resource so thorough and interconnected that search engines can't help but see you as an authority on the topic. This whole process kicks off long before you even think about writing a single word.
Start With Semantic Keyword Research
Forget the old way of finding one high-volume keyword and stuffing it into a page. Semantic keyword research is about mapping out an entire topic. You aren't just hunting for keywords; you're uncovering concepts, questions, and all the related ideas that create a complete picture for a user.
You're trying to get inside your audience's head and anticipate everything they might need to know.
To do this right, you need to:
- Identify Subtopics: Break your main topic down. If your core topic is "content marketing," your subtopics would be things like "content marketing strategy," "building a content calendar," and "measuring content ROI."
- Find Related Questions: Dive into Google's "People Also Ask" section or use tools to find the exact questions your audience is typing into the search bar. Answering these directly is a huge part of semantic SEO.
- Gather Synonyms and Related Terms: Collect all the different ways people talk about your topic. This isn't just synonyms; it includes conceptually related phrases. For "SEO," you'd also want to gather terms like "organic traffic," "search rankings," and "SERPs."
By building this rich collection of terms and questions, you create a blueprint for content that covers a user's query from every possible angle, moving far beyond the limits of a single keyword.
Build Powerful Topic Clusters
Once you've mapped out your topic, it's time to organize it using the topic cluster model. Think of this as the architectural framework for your semantic strategy. It’s what turns a random collection of blog posts into a tightly knit library of expertise.
This structure has two main parts:
- A pillar page: This is your comprehensive, high-level guide on the main topic. It’s the central hub of your cluster.
- Cluster content: These are multiple, in-depth articles that each dive deep into one of the specific subtopics you identified earlier.
The magic happens when every single piece of cluster content links back to the main pillar page. This creates a clear hierarchy that signals your deep expertise to search engines.
Weave a Web of Internal Links
The final piece of the puzzle is smart internal linking. Topic clusters give you the basic structure, but it’s the internal links that forge the strong semantic connections between your pages. Every link is a vote of confidence, telling search engines how your content is related.
When you link between pages, always use descriptive anchor text that clearly explains what the destination page is about. So, instead of a generic "click here," you’d use something like "learn more about our content marketing strategy."
This simple practice helps both users and search engines understand the context of your content. By focusing on creating https://copymasters.co/blog/high-quality-content-for-seo and linking it together intelligently, you build a powerful, context-rich website that search engines love.
Speak Google’s Language with Structured Data
Imagine you’ve written a fantastic article. To you, it’s a story, a guide, a product description. But to a search engine, it's just a wall of text. Structured data, often called schema markup, acts as your official translator. It’s a special vocabulary you add to your website's code that tells search engines exactly what everything means.
Think about a recipe page. Without structured data, Google has to guess that "45 minutes" is the cook time and "4.8/5" is the user rating. With structured data, you’re not leaving it to chance. You're explicitly labeling the key details: "Hey Google, this number, $49.99, is the price, and this number, 4.8, is the average rating from 257 reviews." It completely removes the guesswork.
How Schema Earns You Rich Snippets
This direct line of communication is a huge part of semantic SEO because it adds a layer of undeniable meaning to your content. The most immediate payoff? Rich snippets. These are the eye-catching, beefed-up search results that include star ratings, prices, event dates, or even clickable FAQ sections. They make your listing pop on the page.
Structured data is the technical handshake between your content and the search engine. It confirms you're providing clear, well-organized information, which makes Google see you as a trustworthy source for its most valuable search features.
When you provide this kind of explicit context, you help search engines classify your content with much greater confidence. This directly feeds into building your topical authority, because Google can easily connect your page to the right entities in its massive Knowledge Graph.
A Few of the Most Powerful Schema Types
There are hundreds of schema types out there, but you don't need to know them all. A handful of them are incredibly powerful for most businesses and can give your visibility and click-through rates a serious boost.
- Article Schema: This one is straightforward. It identifies your content as an article and specifies the author, publication date, and headline. It’s your ticket to getting featured in Google’s news carousels and Top Stories.
- FAQPage Schema: Got a page with a list of questions and answers? Use this markup. It makes you eligible for those awesome interactive FAQ rich snippets right on the search results page, taking up more screen space and pushing competitors down.
- Product Schema: If you run an ecommerce site, this is non-negotiable. It details a product’s name, price, availability, and reviews, feeding that info directly into rich snippets that attract qualified buyers before they even click.
And the best part? You don't need to be a coding whiz to get started. Tools like Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper are designed for everyone. You just highlight different elements on your page, tell the tool what they are, and it generates the code for you. It makes one of the most technical-sounding parts of semantic SEO surprisingly easy to implement.
Measuring The Impact Of Your Semantic SEO
So, you've put in the work to build out a semantic SEO strategy. How do you know if it's actually working? Forget obsessively tracking a handful of "money" keywords. That's the old way of thinking.
The real goal here isn't just to hit #1 for one term. It's to own the entire conversation around a topic. When you do it right, your content will start popping up for hundreds, sometimes thousands, of related long-tail questions—queries you didn't even know you were targeting.
Key Performance Indicators For Semantic Success
To get a true read on your performance, you need to look at a different set of signals. Most of this data is waiting for you in Google Search Console and your favorite analytics platform.
- Keyword Breadth: How many unique keywords is a single page or topic cluster ranking for? This number should be constantly climbing, proving Google sees your content as a deep resource.
- Long-Tail Query Growth: Keep a close eye on your rankings for longer, more conversational phrases. This is where semantic SEO really shines, capturing traffic from people who know exactly what they want.
- Rich Snippet CTR: If you’ve added structured data, track the click-through rates on pages that win rich snippets like FAQs, How-tos, or reviews. A higher CTR here is proof that your enhanced SERP listings are grabbing attention.
- Topic Cluster Traffic: Instead of looking at single-page traffic, measure the total organic traffic to all the pages in a topic cluster. This gives you a holistic view of your authority on the subject.
Measuring Your Topical Authority
Another powerful way to gauge your success is by looking at your overall visibility for a subject, often called Share of Voice (SOV). This metric tells you how much of the search real estate your brand owns for an entire topic compared to your competitors.
Share of Voice is more than just rank tracking. It measures your actual dominance in a topical arena, giving you a clear benchmark of how well your semantic strategy stacks up against everyone else.
Once you see why SOV is so important, learning how to calculate your Share of Voice gives you a concrete method for benchmarking your performance. This data not only proves the value of your work but also helps you decide what content to build next.
Still Have Questions About Semantic SEO?
Even with a solid grasp of the basics, a few questions always seem to pop up when it's time to put semantic SEO into action. Let's clear up some of the most common ones.
Is Semantic SEO Just a Fancy Term for LSI Keywords?
Not at all. Thinking that semantic SEO is just about LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords is like saying a car is just a steering wheel. LSI keywords are simply related terms, and they're one tiny piece of a much larger puzzle.
A true semantic strategy goes way deeper. It's about understanding user intent, structuring your content into topic clusters, identifying key entities, and using structured data to give Google the full picture. It’s a holistic approach to building genuine topical authority.
How Long Until I See Results?
Let's be real: this is a long game. Semantic SEO isn't about quick wins or overnight rankings. You're fundamentally changing how search engines perceive your entire website by proving you're an expert on a topic.
Building that kind of comprehensive content and authority takes time—often several months before you see a significant impact. But the payoff is worth it. The results you get are far more stable and less likely to be wiped out by the next Google algorithm update.
Don't chase instant rankings. Semantic SEO is about building lasting authority by actually helping your audience. It's a gradual process, but one that delivers more durable and meaningful results than any short-term tactic ever could.
Can I Apply This to My Existing Content?
Absolutely! In fact, updating your existing content is one of the best ways to start.
Run an audit of what you already have. Look for articles you can beef up to better answer what users are really asking. You can group related posts into powerful topic clusters, add smart internal links to connect the dots, and implement schema markup to give search engines more context. This is often the lowest-hanging fruit for getting started.
- SaaS SEO Consulting for Predictable Growth - October 20, 2025
- What Is SEO Management Your Guide to Real Results - October 19, 2025
- A Guide to Quality Content for SEO That Ranks - October 18, 2025
